Yo, listen up! We’re diving into the world of mortgage loans – fixed rates, adjustable rates, FHA, VA – you name it, we got it! Get ready for a rollercoaster ride of home financing knowledge that’ll have you feeling like a real estate pro in no time.
Now, let’s break it down and see what these different types of mortgage loans are all about.
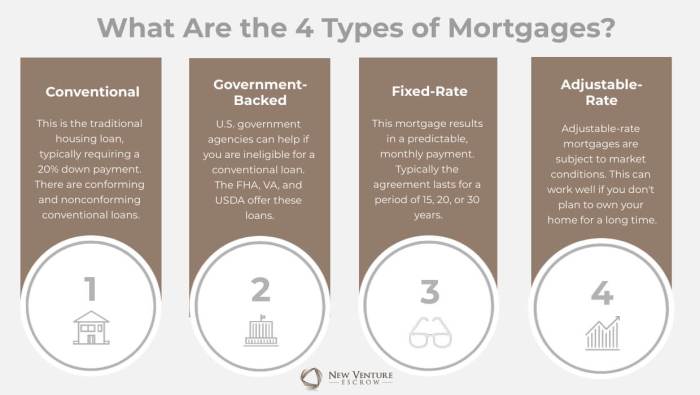
Types of Mortgage Loans
When it comes to getting a mortgage loan, there are several options to choose from based on your financial situation and needs. Let’s dive into the different types of mortgage loans available in the market.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage is a type of loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means your monthly payments will also remain constant, providing predictability and stability for budgeting purposes.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
On the other hand, an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) has an interest rate that can change periodically based on market conditions. This can result in fluctuating monthly payments, making it a riskier option but potentially offering lower initial rates for a certain period.
FHA Loans vs. Conventional Loans
FHA loans are backed by the Federal Housing Administration and typically require lower down payments and credit scores compared to conventional loans. However, they also come with additional fees such as mortgage insurance premiums. Conventional loans, on the other hand, are not backed by the government and may require higher credit scores and down payments, but they often have fewer fees.
VA Loans for Eligible Veterans
VA loans are specifically designed to help eligible veterans, active-duty service members, and their families become homeowners. These loans offer benefits such as no down payment requirements, lower interest rates, and no private mortgage insurance, making them a great option for those who have served in the military.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages are loans where the interest rate remains the same for the entire term of the loan, providing predictability and stability for borrowers.
Typical Term Lengths for Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages typically come in term lengths of 15, 20, or 30 years, with the most common being the 30-year fixed-rate mortgage.
How Interest Rates are Calculated for Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Interest rates for fixed-rate mortgages are determined based on market conditions at the time of loan origination, borrower credit score, loan amount, and the term length chosen by the borrower.
Pros and Cons of Choosing a Fixed-Rate Mortgage
- Pros:
- Predictable monthly payments
- Protection against rising interest rates
- Easy to understand and budget for
- Cons:
- Higher initial interest rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages
- May not be the best choice if the borrower plans to sell the property within a few years
When a Fixed-Rate Mortgage Might Be the Best Choice
If a borrower values stability and predictability in their monthly housing expenses, plans to stay in the home long-term, or wants to avoid the risk of rising interest rates, a fixed-rate mortgage could be the best choice for them.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM)
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages, commonly known as ARMs, are mortgage loans where the interest rate can change over time. This is in contrast to Fixed-Rate Mortgages, where the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan.
Interest Rate Fluctuation in ARMs
In an ARM, the interest rates are tied to a specific financial index, such as the prime rate or the LIBOR rate. This means that as the index fluctuates, so does the interest rate on the loan. Typically, there is an initial fixed-rate period where the interest rate remains constant, after which it can adjust periodically based on the terms of the loan.
- During the fixed-rate period, borrowers can benefit from lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate loans.
- Once the fixed-rate period ends, the interest rate can adjust either up or down, depending on market conditions.
- There are caps in place to limit how much the interest rate can increase or decrease during each adjustment period and over the life of the loan.
Suitability of ARMs for Borrowers
ARMs can be suitable for borrowers who plan to move or refinance before the fixed-rate period ends. They can also benefit borrowers who expect interest rates to decrease in the future or those who are looking for lower initial monthly payments.
- It is essential for borrowers to understand the risks associated with ARMs, including potential payment increases when interest rates rise.
- Before choosing an ARM, borrowers should carefully consider their financial situation, future plans, and risk tolerance.
- Working with a knowledgeable mortgage lender can help borrowers determine if an ARM is the right choice for their specific circumstances.
FHA Loans vs. Conventional Loans
When it comes to choosing between FHA loans and conventional loans, there are some key differences to consider. FHA loans are insured by the Federal Housing Administration, making them more accessible to borrowers with lower credit scores and smaller down payments. On the other hand, conventional loans are not insured by the government and typically require higher credit scores and larger down payments.
Eligibility Criteria for FHA Loans
- Minimum credit score of 580 for a 3.5% down payment
- Debt-to-income ratio of 50% or lower
- Steady employment and income
Down Payment Requirements
- FHA loans require a minimum down payment of 3.5%
- Conventional loans typically require down payments ranging from 5% to 20%
Benefits of Choosing an FHA Loan
- Lower credit score requirements
- Lower down payment requirements
- More lenient debt-to-income ratio
- Fixed interest rates available
VA Loans
VA Loans, or Veterans Affairs loans, are mortgage loans that are guaranteed by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and are designed to help military service members, veterans, and eligible surviving spouses become homeowners. These loans offer many benefits and advantages to those who have served in the military.
Eligibility and Advantages
- Eligibility: VA loans are available to active-duty service members, veterans, reservists, and National Guard members, as well as certain spouses.
- Advantages: One of the main advantages of VA loans is that they often do not require a down payment, making homeownership more accessible. Additionally, VA loans typically do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can help save borrowers money on their monthly payments.
Application Process
- Application: To apply for a VA loan, veterans must obtain a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) from the VA. This document verifies their military service and confirms their eligibility for a VA loan.
- Approval: Once the COE is obtained, veterans can work with a VA-approved lender to complete the loan application process. Lenders will review the veteran’s financial information and credit history to determine loan approval.
Tips for Veterans
- Research: Veterans should take the time to research and compare different VA lenders to find the best loan terms and interest rates.
- Understand Terms: It’s important for veterans to fully understand the terms and conditions of the VA loan, including any fees or costs associated with the loan.
- Consultation: Veterans can seek guidance from VA loan specialists or housing counselors to ensure they make informed decisions throughout the homebuying process.