Diving into the world of loan applications, we unravel the complexities and nuances of the process, shedding light on the ins and outs that applicants need to navigate. From understanding the steps involved to demystifying the key documents required, this exploration promises to be both enlightening and practical.
As we delve deeper, we uncover essential insights that can empower individuals seeking financial assistance through loans.
Overview of the Loan Application Process
When it comes to applying for a loan, there are several key steps involved in the process. From gathering documents to understanding your credit score, each step plays a crucial role in determining your eligibility for a loan.
Steps in the Loan Application Process
- 1. Research Lenders: Start by researching different lenders to find one that suits your needs and offers competitive rates.
- 2. Gather Documents: Prepare key documents such as proof of income, identification, and bank statements.
- 3. Fill out Application: Complete the loan application form provided by the lender, ensuring all information is accurate.
- 4. Credit Check: Lenders will conduct a credit check to assess your creditworthiness and determine the interest rate for your loan.
- 5. Approval Process: Once the application is submitted, the lender will review your documents and credit score to make a decision.
- 6. Receive Funds: If approved, you will receive the funds in your account, and you can start using them for your intended purpose.
Key Documents Required
- – Proof of Income: Pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements to verify your income.
- – Identification: Driver’s license, passport, or other government-issued ID for identity verification.
- – Bank Statements: Statements showing your financial history and ability to repay the loan.
Role of Credit Scores
Your credit score plays a significant role in the loan approval process. It is a numerical representation of your creditworthiness based on your credit history. Lenders use this score to assess the risk of lending to you and determine the interest rate for your loan. A higher credit score indicates lower risk for the lender, making you more likely to be approved for a loan with favorable terms.
Types of Loans and Eligibility Criteria
When it comes to applying for a loan, it’s important to understand the different types of loans available and the eligibility criteria associated with each. This will help you determine which loan best suits your financial needs and ensure that you meet the requirements for approval.
Personal Loans
Personal loans are unsecured loans that can be used for various purposes such as debt consolidation, home improvement, or unexpected expenses. To be eligible for a personal loan, lenders typically look at your credit score, income, employment history, and debt-to-income ratio. The loan amount and interest rate you qualify for will depend on these factors.
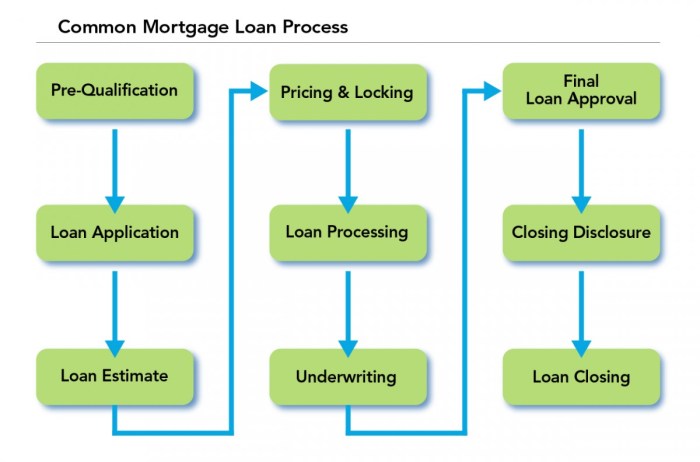
Mortgage Loans
Mortgage loans are used to purchase a home or refinance an existing mortgage. Eligibility criteria for a mortgage loan include credit score, income, employment history, down payment amount, and debt-to-income ratio. Lenders will also consider the type of mortgage (fixed-rate or adjustable-rate) when determining the loan amount and interest rate.
Auto Loans
Auto loans are used to finance the purchase of a vehicle. Eligibility for an auto loan is based on factors such as credit score, income, employment history, down payment amount, and the type of vehicle being purchased. Lenders will also consider the loan term and whether the vehicle is new or used when determining the loan amount and interest rate.
Student Loans
Student loans are designed to help students cover the cost of education. Eligibility for a student loan is typically based on the student’s enrollment status, degree program, and financial need. Lenders may also consider the student’s credit history or require a co-signer. The loan amount and interest rate for student loans can vary depending on these factors.
Online vs. In-Person Loan Applications
When it comes to applying for a loan, you have the option of doing it online or in-person. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to consider your preferences and needs before making a decision.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Here are some points to consider when comparing online and in-person loan applications:
- Online Applications:
- Advantages:
- Convenience: You can apply from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Speed: Online applications are usually processed faster than in-person ones.
- 24/7 Access: You can apply at any time of the day or night.
- Disadvantages:
- Lack of Personal Interaction: You may miss out on the opportunity to ask questions or clarify information face-to-face.
- Potential Security Risks: There is always a risk of data breaches or identity theft when submitting personal information online.
- In-Person Applications:
- Advantages:
- Personalized Assistance: You can get help from a loan officer in-person.
- Clear Communication: You can discuss terms and conditions directly with a representative.
- Disadvantages:
- Time-Consuming: In-person applications may take longer due to waiting times and paperwork.
- Limited Hours: You can only apply during business hours.
Security Measures for Online Applications
Online loan applications may raise concerns about security. Here are some tips to ensure your information is safe:
- Use secure websites with HTTPS encryption.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks when submitting sensitive information.
- Keep your devices and software up to date to prevent malware attacks.
- Monitor your credit report regularly for any suspicious activity.
Tips for Choosing
When deciding between online and in-person loan applications, consider the following:
- Assess your comfort level with technology and online transactions.
- Weigh the importance of personal interaction and assistance in the application process.
- Compare the speed and efficiency of online versus in-person applications based on your needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Loan Application Process
When applying for a loan, it’s crucial to avoid common mistakes that could potentially delay or jeopardize your approval. By being aware of these pitfalls and taking proactive steps to prevent them, you can significantly improve your chances of getting the loan you need. Here are some key mistakes to watch out for and tips on how to avoid them:
Failure to Provide Accurate Information
One of the most common mistakes applicants make is providing inaccurate or incomplete information on their loan application. Lenders rely on the information you provide to make a decision, so any discrepancies or false details can lead to rejection. To avoid this, double-check all your information before submitting the application. Make sure to provide accurate details about your income, employment status, and financial history.
Neglecting to Check Credit Score
Another frequent mistake is not checking your credit score before applying for a loan. Your credit score plays a significant role in determining your eligibility and interest rates. By reviewing your credit report beforehand, you can identify any errors or negative marks that may impact your application. Take steps to improve your credit score if needed before applying for a loan.
Submitting Incomplete Documentation
Incomplete documentation is a major red flag for lenders and can lead to delays in the approval process. Make sure to gather all the required documents, such as pay stubs, bank statements, tax returns, and identification, before submitting your application. Providing a complete set of documentation will streamline the process and demonstrate your readiness to repay the loan.
Ignoring Debt-to-Income Ratio
Your debt-to-income ratio is a crucial factor that lenders consider when evaluating your application. Ignoring this ratio and taking on more debt than you can afford can signal financial instability and lead to rejection. Before applying for a loan, calculate your debt-to-income ratio and ensure it falls within the acceptable range. Paying down existing debts can help improve your ratio and increase your chances of approval.
Failing to Compare Loan Options
Another mistake to avoid is failing to shop around and compare loan options from different lenders. Each lender may offer different terms, interest rates, and fees, so it’s essential to explore your options and choose the best fit for your financial situation. By comparing multiple loan offers, you can secure the most favorable terms and potentially save money in the long run.
Importance of Thorough Documentation and Accuracy
Thorough documentation and accuracy are paramount during the loan application process. Providing precise information and complete documentation not only expedites the approval process but also instills confidence in the lender regarding your creditworthiness. Remember, the more organized and accurate your application, the smoother and quicker the approval process will be.
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
When it comes to taking out a loan, it’s crucial to understand the terms and conditions that come with it. These terms can impact your repayment process and the overall cost of borrowing. Let’s break down some key terminologies and their implications.
Interest Rate
The interest rate is the percentage charged by the lender for borrowing the money. A higher interest rate means you’ll pay more over the life of the loan, increasing the total cost of borrowing.
Loan Term
The loan term is the length of time you have to repay the loan. A longer loan term may result in lower monthly payments but higher overall interest costs. On the other hand, a shorter term means higher monthly payments but less interest paid in total.
Fees and Charges
Various fees and charges may be associated with the loan, such as origination fees, late payment fees, and prepayment penalties. These can add to the overall cost of borrowing, so it’s essential to be aware of them.
Collateral
Collateral is an asset you pledge to secure the loan. If you fail to repay, the lender can seize the collateral. This can affect the terms of the loan, as secured loans typically have lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans.
APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
The APR includes the interest rate and any additional fees charged by the lender. It gives you a better idea of the total cost of borrowing, making it easier to compare different loan offers.