Get ready to dive into the world of calculating debt-to-income ratio. This crucial financial metric plays a key role in assessing your financial health, and we’re here to break it down in a way that’s easy to understand.
As we explore the formula, examples, and interpretations of debt-to-income ratio, you’ll gain valuable insights into managing your finances like a pro.
Understanding Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio is a crucial financial metric that shows the percentage of a person’s monthly income that goes towards paying debts. This ratio is essential for evaluating an individual’s financial health and ability to take on additional debt responsibly.
Types of Debt Included in the Ratio
- Mortgage: Monthly payments towards a home loan.
- Student Loans: Repayments for educational loans.
- Credit Card Debt: Outstanding balances on credit cards.
How Lenders Use the Ratio
Lenders use the Debt-to-Income Ratio to assess a borrower’s capacity to manage more debt. A lower ratio indicates that a person has more disposable income after servicing existing debts, making them less risky to lend to. Typically, lenders prefer to see a ratio below 36%, although specific requirements may vary.
Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
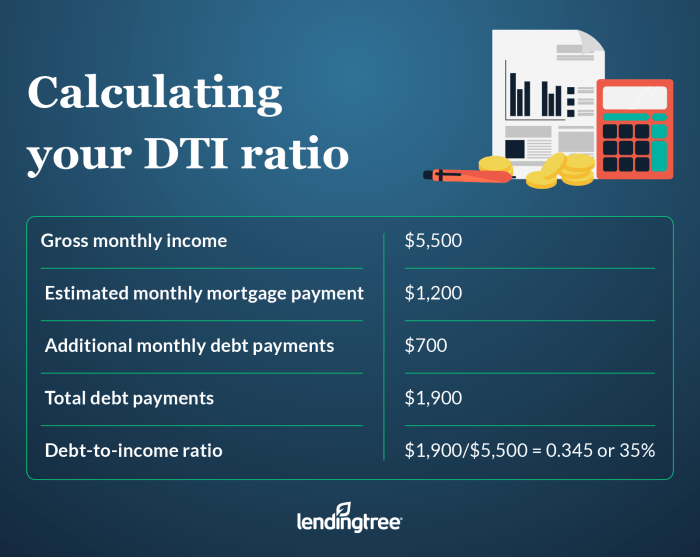
To determine your debt-to-income ratio, you need to follow a specific formula and gather the necessary financial information. This ratio is crucial for lenders to assess your financial health and ability to manage debt effectively.
Formula for Calculating Debt-to-Income Ratio
Debt-to-Income Ratio = (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100
Gathering Necessary Financial Information
- List all your monthly debt payments, including mortgage, car loans, credit card payments, student loans, and any other debts.
- Calculate your total gross monthly income, which includes salary, bonuses, commissions, alimony, and any other sources of income.
Examples of Calculating the Ratio
Let’s say your total monthly debt payments amount to $2,000, and your gross monthly income is $6,000.
Debt-to-Income Ratio = ($2,000 / $6,000) x 100 = 33.33%
In this case, your debt-to-income ratio would be 33.33%, indicating that 33.33% of your gross monthly income goes towards debt payments.
Interpreting Debt-to-Income Ratio Results
When it comes to interpreting debt-to-income ratio results, it’s essential to understand what different ranges of ratios indicate about an individual’s financial situation. Whether the ratio is high or low can significantly impact one’s ability to secure loans or credit, so let’s dive into the details.
Impact of Debt-to-Income Ratio
- A high debt-to-income ratio, typically above 43%, signals that a large portion of income is already allocated to debt payments. This can indicate financial strain and may make it challenging to qualify for additional credit or loans.
- On the other hand, a low debt-to-income ratio, ideally below 36%, shows that a smaller percentage of income is used to cover debts. Lenders often view this favorably as it suggests better financial stability and the ability to manage debt responsibly.
- Having a moderate debt-to-income ratio, falling between 36% to 43%, may still allow for credit approval, but it could come with higher interest rates or stricter terms due to the perceived risk.
Improving Debt-to-Income Ratio
- To improve your debt-to-income ratio, consider paying down existing debts to reduce the total amount owed. This can help lower the ratio and demonstrate better financial health to lenders.
- Avoid taking on new debt unnecessarily, as this can increase your ratio and raise red flags for lenders. Focus on increasing your income or finding ways to decrease expenses to improve the ratio over time.
- Creating a budget and sticking to it can also help you manage your debts more effectively and prevent your ratio from climbing too high. Prioritize paying off high-interest debts first to make a bigger impact on reducing the ratio.
Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratio in Financial Planning
Understanding your debt-to-income ratio is crucial in financial planning as it directly impacts your budgeting and financial goal-setting. This ratio provides a clear picture of how much of your income goes towards paying off debts, helping you manage your finances effectively.
Maintaining a Healthy Debt-to-Income Ratio
Keeping your debt-to-income ratio at a healthy level is essential for financial stability. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Avoid taking on unnecessary debt: Only borrow what you need and can afford to repay.
- Pay off high-interest debts first: Focus on clearing debts with high-interest rates to reduce overall interest payments.
- Increase your income: Look for ways to boost your income through side hustles or career advancement to lower your debt-to-income ratio.
- Create a budget and stick to it: Proper budgeting can help you allocate funds efficiently and prevent overspending.
Using Debt-to-Income Ratio for Long-Term Financial Stability
Utilizing your debt-to-income ratio as a tool for long-term financial stability involves:
- Setting financial goals: Use your debt-to-income ratio to set realistic financial goals and track your progress towards achieving them.
- Monitoring changes: Regularly review your debt-to-income ratio to adapt your financial plan accordingly and make necessary adjustments.
- Seeking professional advice: Consult with a financial advisor for personalized guidance on managing your debt-to-income ratio effectively.