Yo, let’s talk about compounding interest – it’s like the secret sauce in the finance world that can make your money grow exponentially. From understanding the basics to maximizing your returns, this topic is a game-changer.
Now, let’s dive into the formula, benefits, strategies, and differences between compounding interest and simple interest to level up your financial knowledge.
Introduction to Compounding Interest
Compounding interest is a powerful concept in the world of finance that allows your money to grow exponentially over time. It involves earning interest on both the initial principal amount and the accumulated interest from previous periods.
Unlike simple interest, where you only earn interest on the principal amount, compounding interest allows your savings to snowball as interest is continuously added to the total balance.
Example of Compounding Interest
Let’s say you invest $1,000 in an account with an annual interest rate of 5%. At the end of the first year, you would earn $50 in interest, bringing your total balance to $1,050. In the second year, you would earn 5% interest on $1,050 ($52.50), not just on the initial $1,000. This cycle continues, with your money growing at an accelerating rate.
The Formula for Calculating Compounding Interest
When it comes to calculating compounding interest, a specific formula is used to determine the growth of an investment over time. The formula takes into account the principal amount, interest rate, and the length of time the money is invested. Understanding this formula is essential for anyone looking to grow their wealth through investments.
The formula for calculating compound interest is:
A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt)
Where:
– A = the amount of money accumulated after n years, including interest.
– P = the principal amount (initial investment).
– r = annual interest rate (in decimal form).
– n = number of times that interest is compounded per year.
– t = time the money is invested for in years.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Calculate Compounding Interest
To calculate compounding interest, follow these steps:
- Determine the principal amount (P) that you are starting with.
- Identify the annual interest rate (r) that will be applied to the principal amount.
- Determine how many times the interest is compounded per year (n).
- Determine the length of time (t) that the money will be invested for in years.
- Plug these values into the formula A = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) to calculate the total amount of money accumulated after the specified time period.
- Subtract the principal amount from the total amount calculated to find out how much interest has been earned.
Benefits of Compounding Interest
Compounding interest offers several advantages that can significantly impact the growth of an investment over time. By reinvesting the interest earned, you can accelerate the growth of your initial investment, leading to exponential returns.
Increased Wealth Accumulation
- With compounding interest, your money grows at an increasing rate over time, allowing you to accumulate more wealth compared to simple interest.
- Even small regular contributions can lead to substantial gains in the long run, thanks to the power of compounding.
Comparison of Growth
- Let’s consider an example where two individuals invest $10,000 each. One person invests in a savings account with simple interest, while the other chooses a compounding interest investment.
- After 10 years, the individual with compounding interest could potentially have significantly more money due to the compounding effect on their earnings.
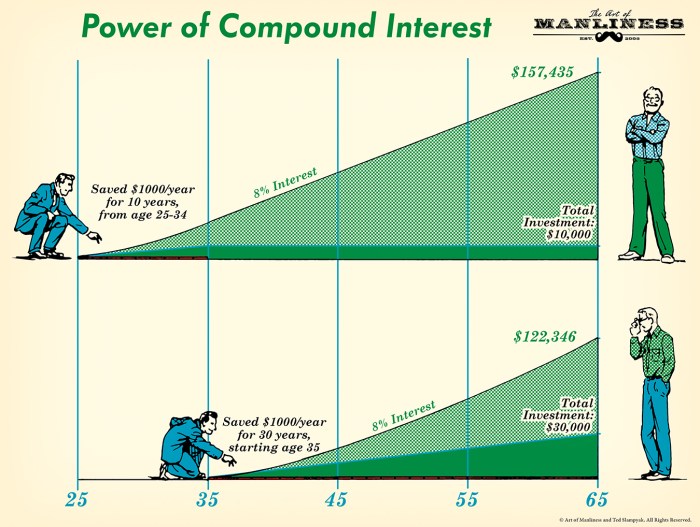
Real-Life Illustration
- Imagine two friends, Alex and Sarah, who both start investing $100 per month at the age of 25.
- Alex chooses an investment with compounding interest, while Sarah opts for a simple interest account.
- Fast forward to when they turn 65, Alex’s investment with compounding interest has grown substantially more than Sarah’s due to the compounding effect over the years.
Strategies to Maximize Compounding Interest
When it comes to maximizing the benefits of compounding interest, there are several strategies you can employ to make your money work harder for you over time.
Increasing the Frequency of Compounding
One effective strategy to boost your returns is to increase the frequency of compounding. The more frequently your interest is compounded, the faster your investment will grow. For example, if you have the option to choose between quarterly compounding or monthly compounding, opt for the latter to accelerate your earnings.
Selecting Investment Vehicles with Compounding Interest
Another key strategy is to carefully select investment vehicles that offer compounding interest. Look for accounts or investments that provide compound interest rather than simple interest. This way, your earnings will be reinvested and generate even more interest over time. Consider options like certificates of deposit (CDs), high-yield savings accounts, or dividend-paying stocks to take advantage of compounding.
Consistent Contributions
Consistently contributing to your investment accounts is crucial for maximizing compounding interest. By regularly adding funds to your investments, you can accelerate the growth of your portfolio and take full advantage of compounding. Set up automatic contributions or make it a habit to invest a portion of your income each month to see significant growth over time.
Diversification
Diversifying your investment portfolio is another strategy to maximize compounding interest. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce risk and increase the potential for higher returns. Consider allocating your funds to a mix of stocks, bonds, and other assets to take advantage of compounding in various markets.
Compounding Interest vs. Simple Interest
When it comes to earning interest on your investments, understanding the differences between compounding interest and simple interest is crucial. Compounding interest allows you to earn interest on both the initial principal amount and the accumulated interest, leading to exponential growth over time. On the other hand, simple interest only calculates interest based on the principal amount, resulting in linear growth.
Key Differences
- Compounding interest earns interest on both the principal and accumulated interest, while simple interest only earns interest on the principal amount.
- Compounding interest leads to exponential growth over time, whereas simple interest results in linear growth.
- Compounding interest is more beneficial for long-term investments, as it maximizes the growth potential of your money.
Beneficial Scenarios
- For long-term investments or savings goals, such as retirement funds or college savings, compounding interest is more beneficial due to its exponential growth nature.
- Simple interest may be suitable for short-term loans or investments where a fixed interest rate is agreed upon, and the focus is on the principal amount.
Comparison Examples
Let’s consider an investment of $1,000 with a 5% annual interest rate:
After 5 years:
– Under simple interest: $1,000 + ($1,000 x 0.05 x 5) = $1,250
– Under compounding interest: $1,000 x (1 + 0.05)^5 = $1,276.28
In this example, you can see how compounding interest results in a higher return compared to simple interest over the same period. This showcases the power of compounding when it comes to growing your investments.