Buckle up, folks! Understanding market cycles is like navigating the ever-changing tides of the financial world. Get ready to dive into the rollercoaster ride of market ups and downs with this engaging exploration.
From defining market cycles to uncovering the factors that influence them, this topic is a deep dive into the heartbeat of the economy.
Overview of Market Cycles
Market cycles are recurring patterns or stages that financial markets go through over time. Understanding market cycles is crucial in the financial world as they impact investment decisions, asset prices, and overall market sentiment. These cycles are driven by various factors such as economic conditions, investor behavior, and geopolitical events.
Stages of a Market Cycle
- Expansion: During this phase, the economy is growing, and investor confidence is high. Stock prices rise, and businesses expand.
- Peak: This is the point where the market reaches its highest point. Investor optimism is at its peak, and asset prices are inflated.
- Contraction: In this stage, economic growth slows down, and investor sentiment starts to decline. Stock prices fall, leading to a market correction.
- Trough: The market hits its lowest point in this phase. Investor confidence is low, and asset prices are undervalued.
Impact of Market Cycles on Industries
- Real Estate: The housing market is heavily influenced by market cycles. During the expansion phase, demand for housing increases, leading to rising prices. In contrast, during a contraction, the housing market experiences a downturn.
- Technology: The tech industry is highly sensitive to market cycles. During the expansion phase, tech stocks tend to perform well as investors seek growth opportunities. However, during a contraction, tech companies may face challenges due to reduced consumer spending.
- Consumer Goods: Market cycles can impact consumer goods companies as well. During an economic downturn, consumers may cut back on discretionary spending, affecting companies in this sector. Conversely, during an expansion, consumer goods companies may see increased demand for their products.
Factors Influencing Market Cycles
When it comes to market cycles, there are several key factors that play a significant role in shaping the direction of the market. These factors include economic indicators, investor sentiment and behavior, as well as external events like geopolitical tensions and technological advancements.
Economic Indicators
- Economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment figures can heavily influence market cycles. Positive economic indicators can lead to increased investor confidence and higher stock prices, while negative indicators can trigger market downturns.
- Interest rates set by central banks also impact market cycles. Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and spending, boosting economic growth and potentially driving stock prices higher.
Investor Sentiment and Behavior
- Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in market cycles. When investors are optimistic about the future outlook of the market, they are more likely to buy stocks and drive prices up. Conversely, pessimistic sentiment can lead to selling pressure and market declines.
- Behavioral biases, such as herd mentality and fear of missing out, can also influence market cycles. These biases can result in market bubbles or crashes as investors react to emotions rather than rational analysis.
External Factors
- Geopolitical events, such as trade wars or political instability, can significantly impact market cycles. Uncertainty stemming from these events can lead to market volatility and investor caution.
- Technological advancements and disruptions can also influence market cycles. Industries experiencing rapid technological change may see shifts in stock prices as investors assess the impact of innovation on company performance.
Understanding Bull and Bear Markets
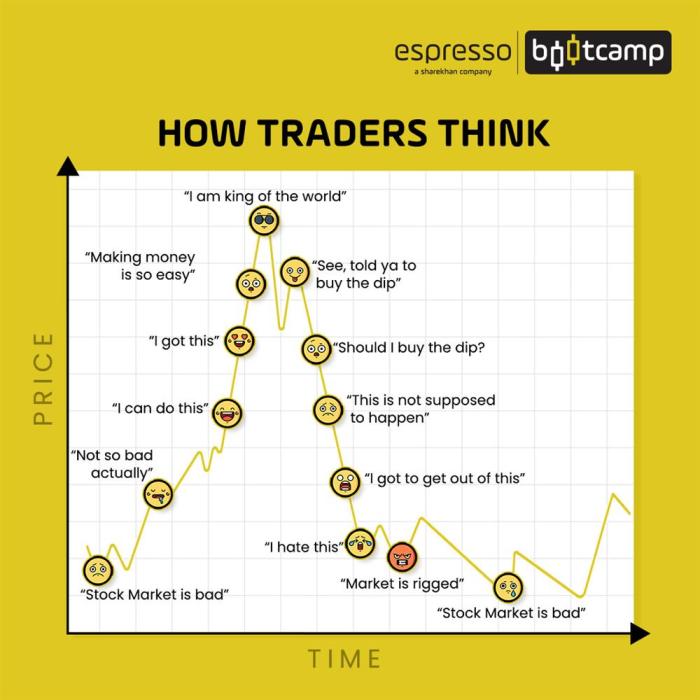
In the context of market cycles, it’s crucial to understand the concepts of bull and bear markets. These terms describe the overall trend of the market, whether it’s on an upward trajectory (bull market) or a downward trend (bear market).
Characteristics of Bull and Bear Markets
- Bull Market:
A bull market is characterized by rising stock prices, investor confidence, and overall optimism in the market. It’s a period of economic expansion where the demand for securities outweighs the supply.
- Bear Market:
On the other hand, a bear market is marked by falling stock prices, pessimism, and a general decline in economic activity. Investors tend to be cautious or sell off their investments during this period.
Strategies for Navigating Bull and Bear Markets
- Diversification:
One effective strategy for navigating both bull and bear markets is diversifying your investment portfolio. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, you can reduce risk and minimize losses during market downturns.
- Long-Term Perspective:
Investors with a long-term perspective are better equipped to ride out the fluctuations of both bull and bear markets. By focusing on the overall growth potential of their investments, they can avoid making hasty decisions based on short-term market movements.
- Stay Informed:
Keeping up with market trends, economic indicators, and global events can help investors make informed decisions in both bull and bear markets. Understanding the factors influencing market cycles is key to developing a successful investment strategy.
Market Cycle Analysis Techniques
In order to analyze market cycles effectively, various technical and fundamental analysis tools are utilized. These tools help investors and traders identify trends and make informed decisions based on market behavior.
:
Technical Analysis Tools
Technical analysis involves using historical price and volume data to predict future market movements. Some common technical analysis tools used to identify market cycles include moving averages and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence).
- Moving Averages: Moving averages are used to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specific period of time. They can help determine the direction of the market cycle by showing whether prices are trending up, down, or sideways.
- MACD: MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. Traders use MACD to identify changes in the strength, direction, momentum, and duration of a market cycle.
Fundamental Analysis Methods
Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating the underlying factors that drive market cycles, such as company earnings reports and economic indicators.
- Earnings Reports: Analyzing a company’s earnings reports can provide insights into its financial health and growth potential. Positive earnings reports can signal an upward trend in the market cycle, while negative reports may indicate a downturn.
- Economic Data: Monitoring economic data, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment figures, can help investors understand the broader economic environment and its impact on market cycles. Changes in economic indicators can influence market trends and cycles.
Pros and Cons of Different Analysis Techniques
When comparing technical and fundamental analysis for market cycle analysis, each approach has its own advantages and limitations.
| Analysis Technique | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Analysis | Provides clear entry and exit signals for trades | May not account for fundamental factors driving market cycles |
| Fundamental Analysis | Offers insights into the underlying value of assets | Can be time-consuming and require in-depth research |