Capital gains tax rates set the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From defining what capital gains tax rates are to exploring the impact on investment decisions, this topic is a rollercoaster ride of financial knowledge.
Delve into the world of capital gains tax rates and discover the intricacies that shape our financial landscape.
Overview of Capital Gains Tax Rates
When it comes to capital gains tax rates, we’re talking about the taxes you pay on the profits you make from selling certain assets like stocks, real estate, or other investments. These rates are determined based on how long you held the asset before selling it and your income level.
Types of Capital Gains Tax Rates
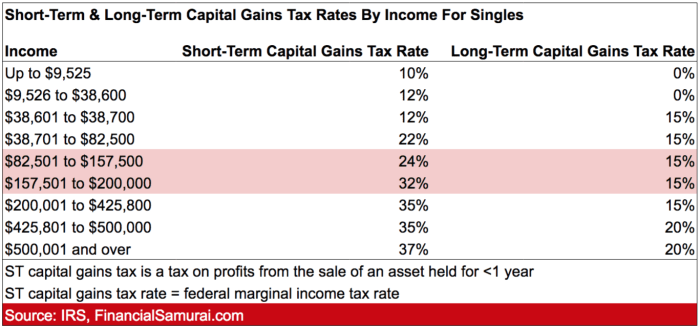
- Short-Term Capital Gains: These are profits made from selling an asset you’ve held for less than a year. They are taxed at your regular income tax rate, which can be as high as 37% for top earners.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: If you held the asset for more than a year before selling it, you qualify for long-term capital gains tax rates. These rates are typically lower than short-term rates, ranging from 0% to 20% depending on your income bracket.
- Qualified Dividends: Certain dividends from stocks and mutual funds are also taxed at the long-term capital gains rate, making them more tax-efficient for investors.
Types of Capital Gains
When it comes to capital gains, there are two main categories: short-term and long-term capital gains. Each type is taxed differently based on the holding period of the asset.
Short-Term Capital Gains
Short-term capital gains are profits earned from the sale of assets held for one year or less. These gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, which can be higher than long-term capital gains tax rates. Examples of assets subject to short-term capital gains tax include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Long-Term Capital Gains
On the other hand, long-term capital gains are profits earned from the sale of assets held for more than one year. These gains are subject to lower tax rates than short-term capital gains. The tax rates on long-term capital gains are typically 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on the taxpayer’s income level. Examples of assets subject to long-term capital gains tax include real estate, collectibles, and precious metals.
Capital Gains Tax Rates vs. Ordinary Income Tax Rates
When it comes to taxes, understanding the difference between capital gains tax rates and ordinary income tax rates is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Let’s dive into how these two types of taxes compare and the impact they have on investments.
Difference Between Capital Gains Tax Rates and Ordinary Income Tax Rates
- Capital gains tax rates are applied to the profits earned from selling assets like stocks, real estate, or other investments held for more than a year. These rates are typically lower than ordinary income tax rates.
- On the other hand, ordinary income tax rates are applied to the money you earn from employment, business income, or interest and dividends. These rates are usually higher than capital gains tax rates.
Comparison of Tax Rates for Capital Gains and Ordinary Income
- For the 2021 tax year, the capital gains tax rates range from 0% to 20%, depending on your income level and filing status. In contrast, ordinary income tax rates can go up to 37% for the highest income earners.
- Investors who fall into the lower tax brackets may benefit from the lower capital gains tax rates, especially if they hold their investments long-term to qualify for the reduced rates.
Impact of Tax Rates on Investment Decisions
- The difference in tax rates between capital gains and ordinary income can influence how investors choose to allocate their assets. Some may opt for investments with the potential for long-term capital gains to take advantage of the lower tax rates.
- Understanding the tax implications is essential for developing a tax-efficient investment strategy that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Impact of Capital Gains Tax Rates on Investments
When it comes to investing, capital gains tax rates play a crucial role in shaping investor behavior and portfolio decisions. These rates can impact the overall return on investment and influence the choices investors make regarding buying, selling, and holding assets.
How Capital Gains Tax Rates Influence Investment Strategies
Capital gains tax rates can affect how investors approach their investment strategies. Higher tax rates on capital gains may discourage investors from selling their assets, as they would have to pay a larger portion of their profits to the government. On the other hand, lower tax rates may incentivize investors to take profits and reallocate their investments.
Examples of Adjustments Investors May Make Based on Tax Rates
- Investors may opt to hold onto their investments for a longer period to qualify for lower long-term capital gains tax rates.
- In anticipation of a potential increase in capital gains tax rates, investors may sell off certain assets before the new rates take effect.
- Some investors may prioritize investing in tax-advantaged accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, to minimize the impact of capital gains taxes.
Impact of Proposed Changes in Capital Gains Tax Rates on the Stock Market
Proposed changes in capital gains tax rates can have a significant impact on the stock market. Uncertainty surrounding potential tax rate hikes or cuts can create volatility and lead to fluctuations in stock prices. Investors may adjust their portfolios in response to these proposed changes, causing shifts in market trends and investor sentiment.