Get ready to dive into the world of bond investment tips, where we’ll uncover strategies to boost your financial portfolio with style and flair. From understanding the basics to mastering risk management, this guide has got you covered.
As we venture deeper, we’ll explore key factors, diversification tactics, and risk mitigation techniques that will elevate your bond investment game to the next level.
Understanding Bond Investments
When it comes to bond investments, it’s all about lending money to an entity, whether it’s a corporation or government, in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of the initial investment amount at a specified maturity date. Bonds are considered a fixed income investment, providing a predictable stream of income.
Types of Bonds
- Corporate Bonds: Issued by corporations to raise capital, these bonds have varying levels of risk depending on the company’s financial health.
- Municipal Bonds: Issued by state and local governments, these bonds are often tax-exempt and considered relatively safe.
- Government Bonds: Issued by the U.S. Treasury, these bonds are considered the safest investment option and include Treasury bonds, notes, and bills.
Risk Factors
- Interest Rate Risk: Bond prices are inversely related to interest rates, so when rates rise, bond prices fall.
- Default Risk: The risk that the issuer may not be able to make interest payments or repay the principal amount.
- Inflation Risk: If the inflation rate is higher than the bond’s yield, the real return on investment decreases.
Comparison with Other Investments
- Stocks: Bonds are considered less risky than stocks but offer lower potential returns.
- Real Estate: Bonds provide a fixed income stream, while real estate investments offer the potential for capital appreciation.
- Savings Accounts: Bonds generally offer higher returns than savings accounts but come with higher risks.
Factors to Consider Before Investing in Bonds
Before diving into the world of bond investments, there are several key factors that you should consider to make informed decisions and maximize your returns.
Interest Rates and Bond Investments
Interest rates play a crucial role in bond investments. When interest rates rise, bond prices tend to fall, and vice versa. This inverse relationship is important to keep in mind as it can impact the value of your bond portfolio.
Importance of Credit Ratings in Bond Investments
Credit ratings provide valuable insights into the creditworthiness of bond issuers. Higher credit ratings indicate lower default risk, while lower ratings suggest higher risk. It’s essential to pay attention to credit ratings to assess the risk associated with a particular bond investment.
Evaluating the Issuer’s Financial Health
Before investing in bonds, it’s crucial to evaluate the financial health of the issuer. Look at key financial metrics such as debt levels, cash flow, and profitability to gauge the issuer’s ability to repay its debt obligations. A strong financial position is a positive indicator for bond investors.
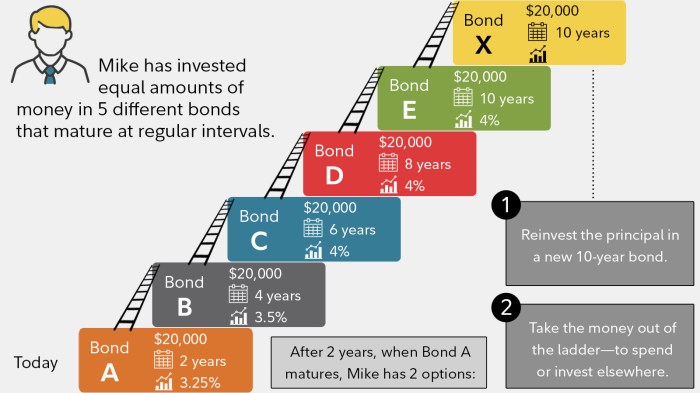
Building a Diversified Bond Portfolio
Diversification is a key strategy in bond investments to reduce risk and optimize returns by spreading out investments across different types of bonds. By diversifying your bond portfolio, you can minimize the impact of negative events that may affect a specific sector or issuer, thereby increasing the overall stability of your investment.
Strategies for Diversifying a Bond Portfolio
- Invest in bonds from various sectors such as government, corporate, municipal, and international bonds.
- Consider bonds with different credit ratings to balance risk and return potential.
- Include bonds with varying maturities to capture opportunities in different interest rate environments.
- Allocate funds across bonds with different durations to manage interest rate risk effectively.
- Explore bonds with different coupon rates to diversify income streams.
Benefits of Investing in Bonds with Different Maturities
- Short-term bonds provide liquidity and stability, ideal for emergency funds or short-term goals.
- Intermediate-term bonds offer a balance between risk and return, suitable for medium-term financial objectives.
- Long-term bonds provide higher potential returns but are exposed to interest rate fluctuations, making them suitable for long-term investment goals.
Tips on Rebalancing a Bond Portfolio
- Regularly review your bond portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
- Adjust your portfolio by selling overperforming bonds and buying underperforming ones to maintain your desired asset allocation.
- Consider market conditions, interest rate changes, and economic outlook when rebalancing your bond portfolio.
- Consult with a financial advisor to get personalized advice on rebalancing strategies based on your specific financial situation.
Managing Risks in Bond Investments
Bond investments come with their own set of risks that investors need to be aware of in order to make informed decisions. It is crucial to understand these risks and have strategies in place to mitigate them effectively.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is a key consideration for bond investors as it refers to the potential impact of changes in interest rates on the value of the bonds. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. To mitigate interest rate risk, investors can consider the following strategies:
- Diversification: By spreading investments across different types of bonds with varying maturities, investors can reduce the impact of interest rate changes on their overall portfolio.
- Investing in Floating Rate Bonds: These bonds have interest payments that adjust periodically based on prevailing market rates, providing a degree of protection against interest rate fluctuations.
- Utilizing Interest Rate Hedging Instruments: Investors can use interest rate swaps or options to hedge against adverse interest rate movements.
Credit Risk
Credit risk refers to the risk of the bond issuer defaulting on interest payments or principal repayment. To manage credit risk, investors can:
- Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on the creditworthiness of bond issuers before investing.
- Invest in Investment-Grade Bonds: These bonds are issued by companies with higher credit ratings, reducing the likelihood of default.
- Diversify Across Issuers: Spreading investments across multiple issuers can help mitigate the impact of a single issuer defaulting.
Inflation Risk
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of bond returns over time. To hedge against inflation risk, investors can consider:
- Investing in Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS): TIPS are specifically designed to protect against inflation by adjusting their principal value based on changes in the Consumer Price Index.
- Investing in Real Assets: Real assets like real estate or commodities can provide a hedge against inflation as their value tends to rise with inflation.
- Shortening Bond Duration: Investing in bonds with shorter durations can help reduce the impact of inflation on bond returns.